
The process begins with identifying the accounts that are likely to become uncollectible. This involves analyzing historical data, customer creditworthiness, and current economic conditions. In accrual-basis accounting, recording the allowance for doubtful accounts at the same time as the sale improves the accuracy of financial reports. The projected bad debt expense is properly matched against the related sale, thereby providing a more accurate view of revenue and expenses for a specific period of time. In addition, this accounting process prevents the large swings in operating results when uncollectible accounts are written off directly as bad debt expenses.
Balance Sheet Aging of Receivables Method for Calculating Bad Debt Expenses
- For example, it has 100 customers, but after assessing its aging report decides that 10 will go uncollected.
- Let’s say your business brought in $60,000 worth of sales during the accounting period.
- For example, a customer takes out a $15,000 car loan on August 1, 2018 and is expected to pay the amount in full before December 1, 2018.
- Tracking doubtful accounts provides an accurate representation of a company’s financial health and ensures compliance with accounting principles.
Recording the amount here allows the management of a company to immediately see the extent of the expected bad debt, how is sales tax calculated and how much it is offsetting the company’s account receivables. Doubtful accounts are considered to be a contra account, meaning an account that reflects a zero or credit balance. In other words, if an amount is added to the “Allowance for Doubtful Accounts” line item, that amount is always a deduction. As a result, the estimated allowance for doubtful accounts for the high-risk group is $25,000 ($500,000 x 5%), while it’s $15,000 ($1,500,000 x 1%) for the low-risk group. Thus, the total allowance for doubtful accounts is $40,000 ($25,000 + $15,000). This transaction doesn’t affect individual customer accounts—every customer still officially owes its full balance.

The Accounts Receivable Performance Toolkit
- Understanding how businesses account for potential failures to pay makes how a firm manages risk far clearer.
- Later, a customer who purchased goods totaling $10,000 on June 25 informed the company on August 3 that it already filed for bankruptcy and would not be able to pay the amount owed.
- Modern accounting software often includes analytics tools that can track and visualize changes in doubtful accounts over time.
- Use an allowance for doubtful accounts entry when you extend credit to customers.
- In contrast, under the allowance method, a business will make an estimate of which receivables they think will be uncollectable, usually at the end of the year.
- The balance sheet will now report Accounts Receivable of $120,500 less the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts of $10,000, for a net amount of $110,500.
If you use double-entry accounting, you also record the amount of money customers owe you. Allowance for uncollectible accounts is an estimate of the portion of accounts receivable that is expected to become uncollectible. The allowance method represents accounts receivable that a company has justifiable reason to believe it may not collect in full or at all. At the end of an Bookkeeping for Painters accounting period, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts reduces the Accounts Receivable to produce Net Accounts Receivable. Note that allowance for doubtful accounts reduces the overall accounts receivable account, not a specific accounts receivable assigned to a customer. Because it is an estimation, it means the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible is not yet known.
- It can also be referred to as Allowance for Uncollectible Expense, Allowance for Bad Debts, Provision for Bad Debts or Bad Debt Reserve.
- Let’s explore the importance of allowance for doubtful accounts, the methods of estimating it, and how to record it.
- He has a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from Ohio State University and previously worked in the financial services sector for JP Morgan Chase, Royal Bank of Scotland, and Freddie Mac.
- They can do this by looking at the total sales amounts for each year, and total unpaid invoices.
- This involves analyzing historical data, customer creditworthiness, and current economic conditions.
- It represents an estimate of the portion of accounts receivable that is expected to become uncollectible due to various reasons, such as customer insolvency, bankruptcy, or inability to pay.
Is Allowance for Doubtful Accounts a Current Asset?
In contrast, under the allowance method, a business will make an estimate of which receivables they think will be uncollectable, usually at the end of the year. This is so that they can ensure costs are expensed in the same period as the recorded revenue. And, having a lot of bad debts drives down the amount of revenue your business should have.
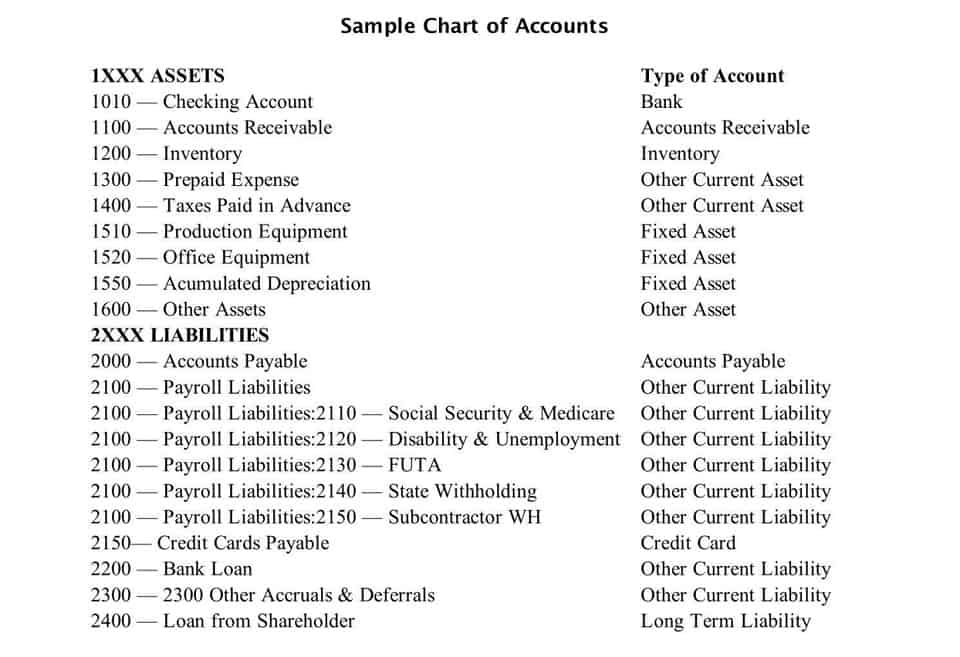
Key differences between doubtful accounts and bad debt
Evidence suggests that some companies have great difficulty in estimating collectibility. Accountants potentially benefit by using additional tools that shed light on the accuracy of past estimates. Allowance for doubtful accounts is essential for finance teams because, in the course of business, companies face multiple risks. Customers might short pay their invoices, raise disputes that delay payments, declare bankruptcy, etc.
Accounts receivable aging method
If a customer ends up paying (e.g., a collection agency collects their payment) and you have already written off the money they owed, you need to reverse the account. For many business allowance for doubtful accounts normal balance owners, it can be difficult to estimate your bad debt reserve. If the doubtful debt turns into a bad debt, record it as an expense on your income statement. Bad debt should be written off when it is determined that a specific account receivable is uncollectible. This decision is typically made after exhausting all reasonable collection efforts and assessing the customer’s financial situation.
